What is the Endocannabinoid System (ECS)?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a fascinating and complex biological system that plays a crucial role in regulating many physiological processes within the human body. The ECS consists of a network of receptors, enzymes, and endocannabinoids that work together to help maintain homeostasis and promote overall health and wellness.
At the heart of the ECS are the endocannabinoids themselves.
These are naturally occurring compounds that are produced by the body to help regulate a wide range of physiological processes, including mood, appetite, sleep, and immune function. The two primary endocannabinoids are anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), both of which are lipid molecules that are synthesized from phospholipid precursors in the cell membrane.
Endocannabinoids are produced on demand and act as retrograde messengers, meaning that they are released by the postsynaptic neuron and act on presynaptic neurons to regulate the release of neurotransmitters. This process helps to maintain a balance of neuronal activity within the body and is critical for overall health and well-being.
In addition to endocannabinoids, the ECS also includes several different types of receptors. These include CB1 receptors, which are primarily found in the brain and central nervous system, and CB2 receptors, which are primarily found in immune cells and other peripheral tissues throughout the body. These receptors play a crucial role in helping to modulate the effects of endocannabinoids and other compounds that interact with the ECS.
The ECS also includes a number of different enzymes that are involved in the synthesis and breakdown of endocannabinoids. These enzymes include fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), which breaks down anandamide, and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL), which breaks down 2-AG. These enzymes help to regulate the levels of endocannabinoids within the body and ensure that they are able to perform their essential functions.
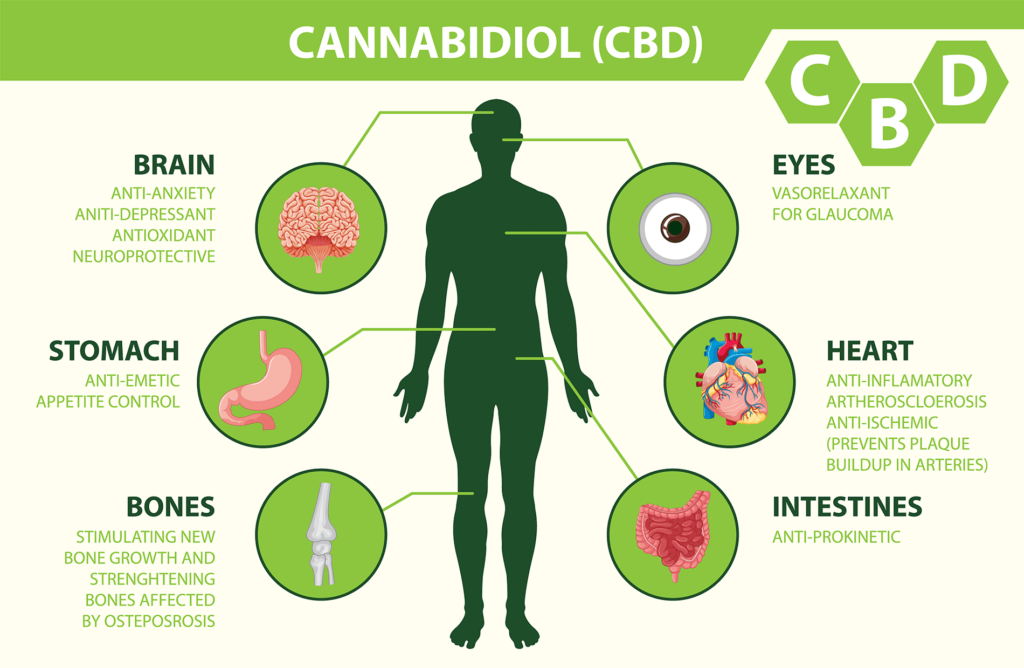
The functions of the ECS are many and varied, and include the regulation of pain and inflammation, mood and anxiety, appetite and metabolism, and sleep and wakefulness. Endocannabinoids are known to have powerful anti-inflammatory effects, which can help to reduce pain and inflammation throughout the body. They also play a key role in the regulation of mood and anxiety, and may help to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety disorders. The ECS also plays a crucial role in the regulation of appetite and metabolism.
Endocannabinoids are known to interact with CB1 receptors in the hypothalamus, which is the part of the brain that controls hunger and satiety. This interaction helps to regulate appetite and ensure that the body is able to maintain a healthy weight and energy balance. Finally, the ECS is also involved in the regulation of sleep and wakefulness.
Endocannabinoids are known to promote deep, restful sleep, and may help to reduce symptoms of insomnia and other sleep disorders. They also play a role in the regulation of circadian rhythms, which help to ensure that the body is able to maintain a healthy sleep-wake cycle.
Overall, the endocannabinoid system is a fascinating and complex biological system that plays a crucial role in regulating many different physiological processes within the body. By understanding the functions of the ECS and how it interacts with other systems within the body, researchers may be able to develop new treatments and therapies for a wide range of health conditions and diseases.




